How To Disable Hardware Acceleration In Chrome
Google Chrome is renowned for its speed and efficiency, often leveraging hardware acceleration to enhance performance. While this feature is beneficial for most users, there may be instances where disabling hardware acceleration is necessary. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of disabling hardware acceleration in Chrome, shedding light on its implications and offering alternative solutions.
Understanding Hardware Acceleration in Chrome
Hardware acceleration in Chrome refers to the process of offloading certain tasks from the CPU to the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) or other specialized hardware components. This optimization technique aims to improve the browser’s performance, especially when handling complex graphics, animations, and multimedia content.
Chrome's hardware acceleration utilizes the GPU's parallel processing capabilities to handle resource-intensive tasks, allowing the CPU to focus on other critical operations. As a result, users often experience smoother scrolling, faster video playback, and improved overall responsiveness.
Benefits of Hardware Acceleration
The advantages of hardware acceleration are significant, particularly for users who frequently engage with visually demanding websites or applications. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhanced Multimedia Experience: Smooth video playback, crisp graphics, and fluid animations enhance the overall multimedia experience.
- Improved Browser Responsiveness: By offloading tasks to the GPU, Chrome can handle multiple processes simultaneously, reducing lag and improving overall responsiveness.
- Efficient Resource Management: Hardware acceleration optimizes resource allocation, ensuring that the CPU's processing power is reserved for critical tasks, leading to improved system performance.
When to Disable Hardware Acceleration
Despite its benefits, there are scenarios where disabling hardware acceleration might be necessary. Here are some common situations:
- Compatibility Issues: Certain websites or web applications may not function correctly when hardware acceleration is enabled. Disabling it can help troubleshoot compatibility problems.
- Performance Degradation: In rare cases, hardware acceleration might lead to unexpected performance issues or system instability. Disabling it can help identify and resolve such problems.
- Power Management: For laptops or devices with limited battery life, disabling hardware acceleration can conserve power, leading to extended battery usage.
- Testing and Development: Web developers may need to disable hardware acceleration to test and debug their websites or applications in a controlled environment.
Step-by-Step Guide: Disabling Hardware Acceleration in Chrome
Follow these simple steps to disable hardware acceleration in Chrome:
- Open Google Chrome on your device.
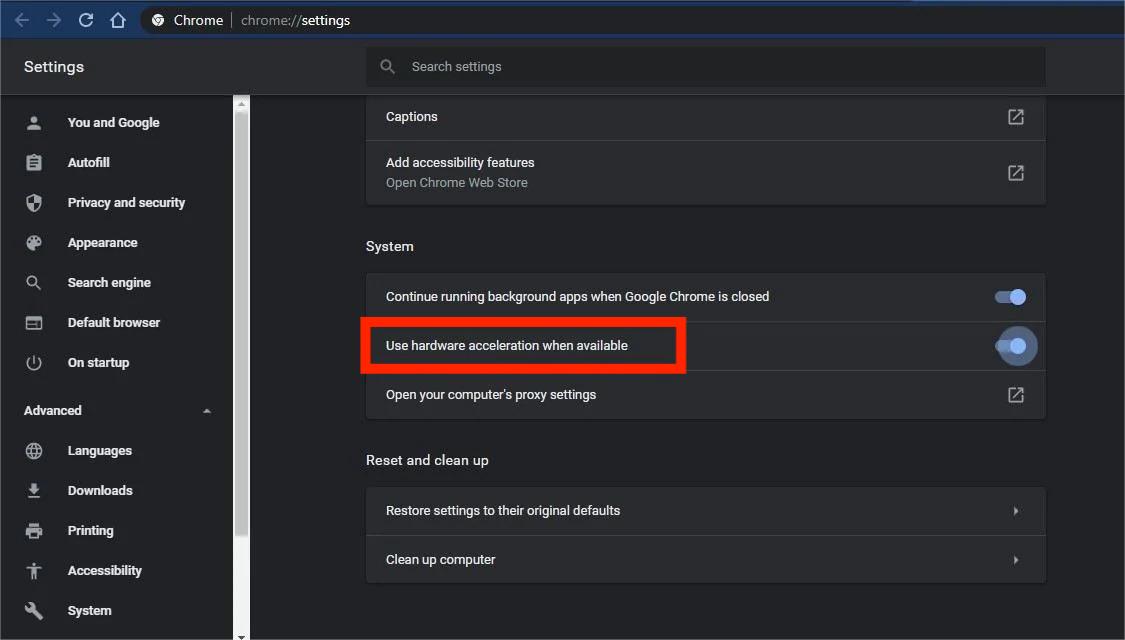
- Click on the three dots in the top-right corner to open the Settings menu.
- Scroll down and click on Advanced to expand the advanced settings.
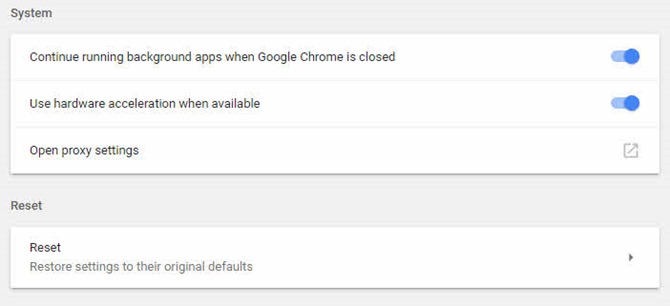
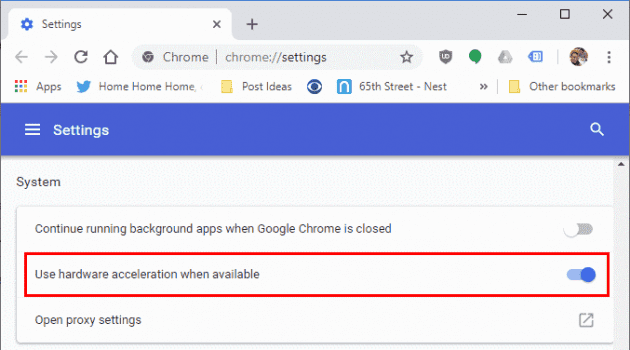
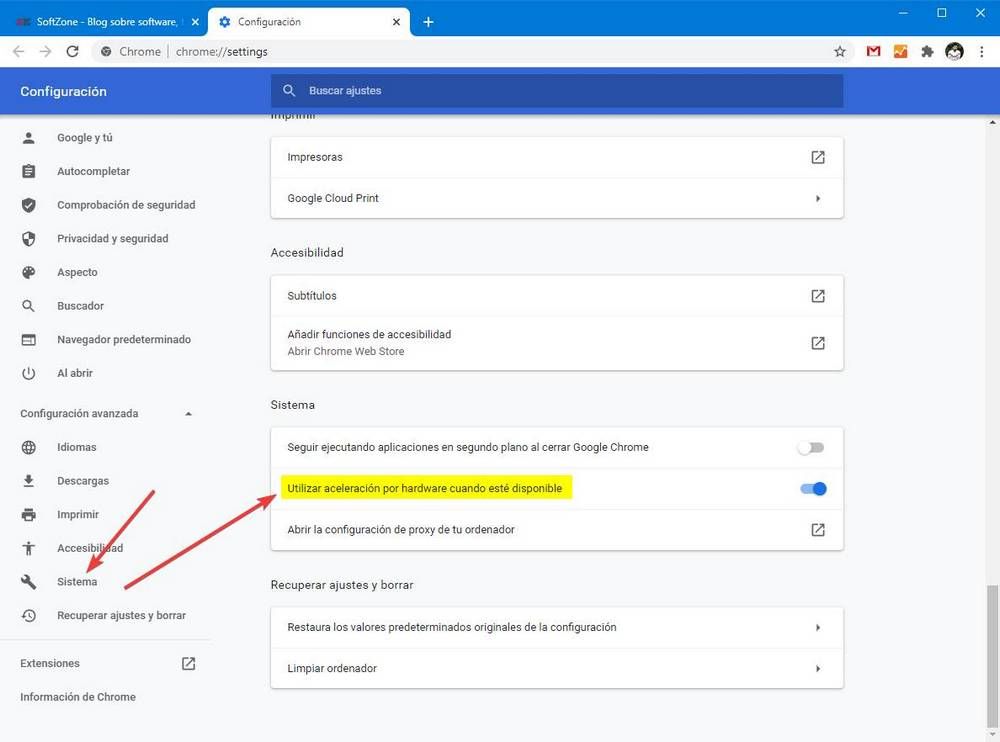
- Under the System section, find the Use hardware acceleration when available option.
- Toggle the switch to Off to disable hardware acceleration.
- Restart Chrome for the changes to take effect.
By following these steps, you can effectively disable hardware acceleration in Chrome. It's important to note that disabling this feature may impact the browser's performance, especially when handling multimedia content. Therefore, it's recommended to disable hardware acceleration only when necessary and explore alternative solutions first.
Alternative Solutions to Consider
Before disabling hardware acceleration, it’s worth exploring other potential solutions to address any issues you might be facing. Here are some alternatives to consider:
- Update Chrome: Ensure that you have the latest version of Chrome installed. Updates often include bug fixes and performance enhancements that can resolve compatibility issues.
- Clear Cache and Cookies: Clearing your browser's cache and cookies can help resolve certain compatibility problems and improve overall browser performance.
- Adjust Other Settings: Chrome offers various settings that can impact performance. Experiment with different options, such as reducing the number of open tabs or adjusting the browser's resource usage settings.
- Use Incognito Mode: Incognito mode disables extensions and temporary settings, providing a clean environment to test whether the issue is related to hardware acceleration or other factors.
- Contact Website Support: If you're experiencing compatibility issues with a specific website, consider reaching out to the website's support team for assistance. They may provide guidance or suggest workarounds.
Performance Analysis: Impact of Disabling Hardware Acceleration
Disabling hardware acceleration in Chrome can have a noticeable impact on the browser’s performance, especially when handling multimedia content. Here’s a closer look at the potential effects:
Video and Animation Performance
With hardware acceleration disabled, Chrome relies solely on the CPU to process video and animation tasks. This can lead to reduced frame rates and less fluid playback, especially for high-definition videos or complex animations. Users may experience slight stuttering or lag during video playback or while interacting with animated elements.
| Setting | Video Performance |
|---|---|
| Hardware Acceleration Enabled | Smooth and fluid video playback with minimal lag. |
| Hardware Acceleration Disabled | Slightly reduced frame rates and potential stuttering during playback. |
Graphics Rendering
Graphics rendering, such as high-quality images or intricate graphical interfaces, may also be impacted. Without hardware acceleration, the CPU takes on the responsibility of rendering these elements, which can result in slightly longer load times and reduced visual quality. Users might notice a subtle difference in the sharpness and clarity of graphics.
Overall Browser Responsiveness
While the impact on overall browser responsiveness may be minimal, it’s worth noting that disabling hardware acceleration can lead to slightly slower response times. Tasks like scrolling through web pages or switching between tabs might feel slightly less smooth compared to when hardware acceleration is enabled.
Power Consumption
One notable advantage of disabling hardware acceleration is reduced power consumption. Since the GPU is not actively involved in processing tasks, the device’s overall power draw decreases. This can be particularly beneficial for laptops or devices with limited battery life, extending their usage time.
Future Implications and Recommendations
The decision to disable hardware acceleration should be made with careful consideration of its potential impact on your browsing experience. Here are some recommendations and implications to keep in mind:
Try Alternative Solutions First
Before disabling hardware acceleration, exhaust other potential solutions. Updating Chrome, clearing cache and cookies, and adjusting other settings can often resolve compatibility issues without sacrificing performance.
Monitor Performance and Compatibility
After disabling hardware acceleration, closely monitor your browsing experience. Pay attention to any performance degradation or compatibility issues that might arise. If problems persist, consider re-enabling hardware acceleration and exploring other troubleshooting methods.
Consider Device-Specific Factors
The impact of disabling hardware acceleration can vary based on your device’s hardware capabilities. Older devices or those with limited processing power may experience more noticeable performance declines. Consider your device’s specifications and make an informed decision accordingly.
Keep Chrome Updated
Regularly update Chrome to ensure you have access to the latest features, improvements, and bug fixes. Chrome developers continuously work on optimizing hardware acceleration and addressing compatibility issues, so staying up-to-date can mitigate potential problems.
Seek Professional Assistance
If you’re unsure about the impact of disabling hardware acceleration or encounter persistent issues, consider seeking assistance from a professional. IT experts or technical support teams can provide personalized guidance and help troubleshoot specific problems.
Conclusion
Disabling hardware acceleration in Chrome is a straightforward process, but it’s essential to understand its potential impact on your browsing experience. While it can resolve compatibility issues and conserve power, it may also lead to performance degradation, especially when handling multimedia content. By following the steps outlined in this guide and considering alternative solutions, you can make an informed decision about whether to disable hardware acceleration in Chrome.
Can I enable hardware acceleration again if needed?
+Yes, you can easily re-enable hardware acceleration in Chrome. Simply follow the same steps as disabling it but toggle the switch to On instead. This will allow Chrome to leverage hardware acceleration once again, improving performance for multimedia content and other tasks.
Will disabling hardware acceleration affect my internet speed?
+Disabling hardware acceleration primarily affects the browser’s internal processing and rendering capabilities. It should not have a direct impact on your internet speed. However, if you’re experiencing slow internet speeds, consider troubleshooting your network connection or contacting your internet service provider.
Are there any security implications when disabling hardware acceleration?
+Disabling hardware acceleration does not introduce any direct security risks. However, it’s always important to maintain a secure browsing environment by keeping your browser, operating system, and security software up-to-date. Regularly scan for malware and practice safe browsing habits to minimize potential threats.