Quicktime After Effects File Size Limit
The world of digital media production often faces challenges related to file management and optimization. One such challenge is encountered when working with QuickTime files in Adobe After Effects. This article aims to delve into the specifics of the QuickTime After Effects file size limit, providing an in-depth analysis, real-world examples, and industry insights to help content creators navigate this aspect of their workflow efficiently.
Understanding the QuickTime After Effects File Size Limit

QuickTime, a multimedia format developed by Apple, is widely used for video and audio files. When importing and exporting media in Adobe After Effects, a popular digital motion graphics and compositing software, users may encounter limitations on the size of QuickTime files.
These limitations can be attributed to a combination of factors, including the technical specifications of the file format, the software's processing capabilities, and the system's hardware configuration. While After Effects can handle large projects with multiple layers and complex effects, the file size limit for QuickTime exports can sometimes pose a challenge, especially for high-resolution, lengthy video sequences.
Technical Specifications and Factors Affecting File Size
The file size of a QuickTime video is influenced by several factors, such as the resolution, frame rate, color depth, and the type of compression used. For instance, a 4K video at 60 frames per second with a high bit rate will result in a significantly larger file size compared to a 1080p video at 30 fps with a lower bit rate.
Furthermore, the compression method plays a vital role. While lossless compression methods, like Apple ProRes, can preserve image quality, they also result in larger file sizes. In contrast, lossy compression formats, like H.264 or HEVC, achieve smaller file sizes by sacrificing some image quality.
| Compression Format | File Size Impact |
|---|---|
| Apple ProRes 422 HQ | Larger file size, high quality |
| H.264 | Smaller file size, some quality loss |
| HEVC (H.265) | Very small file size, moderate quality loss |
The choice of compression format depends on the specific requirements of the project. For instance, if the video is intended for high-quality, professional use, a lossless format like ProRes is preferred. On the other hand, for web delivery or mobile streaming, a lossy format like H.264 can be more suitable, balancing file size and quality.
After Effects’ Handling of Large QuickTime Files
Adobe After Effects has evolved to handle large projects efficiently. It utilizes RAM and hard drive space effectively, allowing users to work with high-resolution footage and complex animations. However, when it comes to exporting QuickTime files, the software may encounter limitations based on the system’s hardware configuration and the chosen export settings.
The software's ability to handle large files also depends on the project's complexity. A simple project with minimal layers and effects may be exported as a large QuickTime file without issues. However, a complex project with numerous layers, effects, and lengthy animations can push the limits of the system's processing power and storage capacity.
Strategies to Optimize QuickTime File Sizes in After Effects
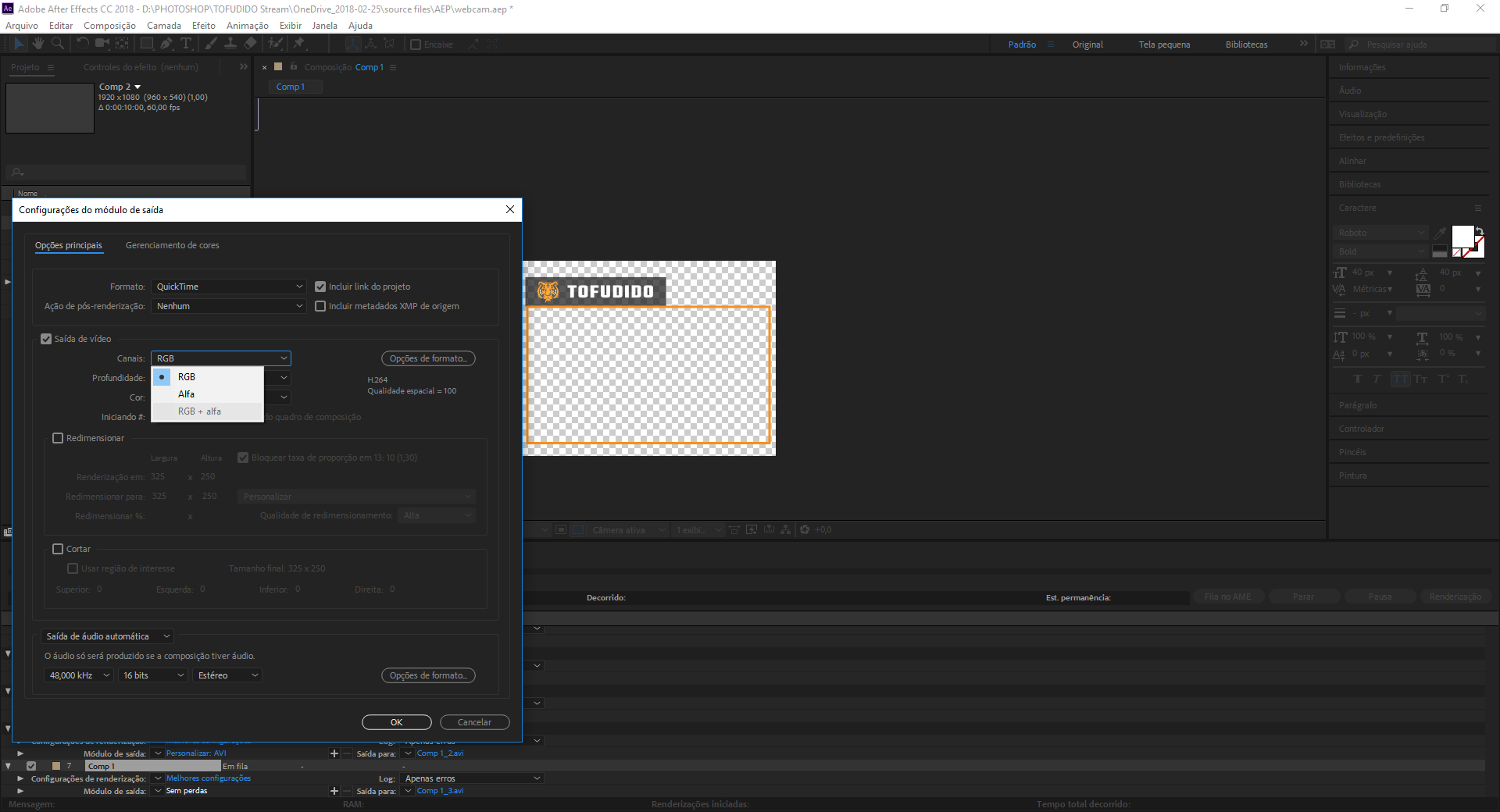
To overcome the challenges posed by the QuickTime After Effects file size limit, content creators can employ various optimization strategies. These strategies not only help in reducing file sizes but also improve the overall efficiency of the production workflow.
Choose the Right Compression Format
As mentioned earlier, the choice of compression format significantly impacts the file size. While lossless formats like Apple ProRes offer high-quality output, they may not be suitable for all scenarios, especially when file size is a concern. In such cases, content creators can opt for lossy compression formats like H.264 or HEVC, which provide smaller file sizes at the cost of some quality.
For instance, a 4K video exported using Apple ProRes 422 HQ can result in a file size of several gigabytes. In contrast, the same video, when exported using H.264 with a moderate bit rate, can be reduced to a few hundred megabytes without a noticeable drop in quality for most viewing scenarios.
Optimize Export Settings
After Effects provides a wide range of export settings that can be customized to suit specific project needs. By optimizing these settings, content creators can significantly reduce the file size of their QuickTime exports without compromising on quality.
One crucial setting is the frame rate. Lowering the frame rate, especially for animations or videos without fast motion, can result in substantial file size reduction. For instance, a 60 fps video can be exported at 30 fps or even 24 fps without a significant impact on the perceived quality.
Another setting to consider is the video bit rate. Lowering the bit rate can lead to smaller file sizes, but it may also result in a loss of detail and quality. Finding the right balance between bit rate and quality is essential for achieving optimal results.
Additionally, After Effects allows users to specify the keyframe interval. A shorter keyframe interval results in larger file sizes, as more frames are treated as keyframes. By increasing the keyframe interval, content creators can reduce the file size without sacrificing the video's smoothness.
Pre-Compose and Optimize Layers
Pre-composing is a powerful technique in After Effects that involves combining multiple layers into a single composition. By pre-composing layers, especially those with complex animations or effects, content creators can reduce the overall file size of the project.
When pre-composing, it's essential to optimize the individual layers. This includes reducing the layer's size and simplifying its animation curves. For instance, a layer with a complex path animation can be optimized by reducing the number of keyframes and using easier-to-compute curves.
Utilize Render Queues and Batch Processing
After Effects’ render queue feature allows users to batch process multiple exports, which can be particularly useful when dealing with large projects. By setting up a render queue, content creators can automate the export process, saving time and effort.
Additionally, the render queue allows for the creation of multiple output formats and sizes. This is especially beneficial when the video needs to be delivered in different resolutions or formats for various platforms or devices.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the impact of the QuickTime After Effects file size limit and the effectiveness of the optimization strategies, let’s explore a few real-world examples and case studies.
Case Study: High-Resolution Animation for Web Delivery
A digital media agency was tasked with creating a high-resolution animated video for a client’s website. The video, featuring complex 3D animations and visual effects, was originally exported as a QuickTime file with Apple ProRes 422 HQ compression. The resulting file size was over 2 GB, which was too large for web delivery.
By optimizing the export settings, the agency was able to reduce the file size significantly. They lowered the frame rate from 60 fps to 30 fps and reduced the bit rate from 120 Mbps to 60 Mbps. Additionally, they utilized H.264 compression instead of ProRes. These changes resulted in a final file size of just under 500 MB, making it suitable for web delivery without compromising on visual quality.
Example: Optimizing a Complex Visual Effects Project
A visual effects artist was working on a complex project involving numerous layers, particle effects, and 3D animations. The initial QuickTime export, using Apple ProRes 4444, resulted in a file size of over 10 GB. This was far beyond the client’s storage capacity and posed challenges for delivery.
To optimize the file size, the artist employed a combination of strategies. They pre-composed several complex layers, simplifying their animations and reducing their size. Additionally, they increased the keyframe interval and lowered the bit rate. These optimizations, coupled with the use of H.264 compression, resulted in a final file size of approximately 3 GB, making it more manageable for delivery and storage.
Industry Insights and Future Implications
The challenge of managing QuickTime After Effects file sizes is a common concern in the digital media production industry. While the software and hardware capabilities continue to evolve, allowing for larger and more complex projects, the need for efficient file management remains critical.
As the industry moves towards higher resolutions, such as 8K and beyond, the file size limit will become an even more prominent issue. Content creators will need to adopt advanced optimization strategies and stay updated with the latest software and hardware advancements to ensure efficient workflow management.
Moreover, with the increasing popularity of streaming platforms and web-based content delivery, the need for smaller file sizes without compromising on quality will continue to drive innovation in compression technologies and export settings.
FAQ

What is the maximum file size limit for QuickTime exports in After Effects?
+
After Effects does not have a specific file size limit for QuickTime exports. However, the file size can be influenced by various factors, such as resolution, frame rate, compression format, and the system’s hardware configuration. In practice, the limit is often determined by the available hard drive space and the system’s ability to process and export the file.
Can I export a large QuickTime file in After Effects without issues?
+
Yes, it is possible to export large QuickTime files in After Effects. However, the success of the export depends on several factors, including the project’s complexity, the chosen compression format, and the system’s hardware configuration. For very large files, it is recommended to optimize the export settings and consider pre-composing layers to reduce the file size.
What is the best compression format for QuickTime exports in After Effects?
+
The best compression format depends on the specific requirements of the project. Lossless formats like Apple ProRes offer high-quality output but result in larger file sizes. Lossy formats like H.264 or HEVC provide smaller file sizes at the cost of some quality. For professional use, lossless formats are preferred, while for web delivery or streaming, lossy formats can be more suitable.
How can I reduce the file size of a QuickTime export in After Effects?
+
To reduce the file size of a QuickTime export, you can optimize various settings in After Effects. This includes lowering the frame rate, reducing the bit rate, increasing the keyframe interval, and using a more efficient compression format. Additionally, pre-composing layers and optimizing their animations can further reduce the file size.
Are there any limitations when exporting QuickTime files with After Effects?
+
Yes, there can be limitations when exporting QuickTime files with After Effects. These limitations are often related to the system’s hardware configuration, available storage space, and the project’s complexity. In some cases, very large or complex projects may exceed the system’s processing capabilities, resulting in failed exports or slow rendering times.