7 Essential Auto Parts Tutorial Tips for Beginners
For novice car enthusiasts, understanding the basics of auto parts is crucial for maintenance, repairs, and customization. Whether you're looking to save on repair costs, enhance your vehicle's performance, or simply gain a deeper appreciation for how cars work, starting with the essentials is key. This guide provides seven indispensable tips to help beginners navigate the world of auto parts effectively. From identifying components to understanding their functions, these insights will empower you to make informed decisions and take the first steps toward automotive proficiency.
1. Familiarize Yourself with Core Auto Components
Every vehicle comprises thousands of parts, but beginners should focus on core components that are critical for operation and safety. The engine, transmission, braking system, suspension, and exhaust system are fundamental. For instance, the engine converts fuel into motion, while the transmission controls power distribution to wheels. Understanding these systems’ roles helps in diagnosing issues and selecting the right parts for replacements or upgrades.
Key Components to Know
Start by learning about the alternator, battery, spark plugs, and filters (air, oil, fuel). These parts are frequently replaced and directly impact performance. For example, a failing alternator can drain the battery, while clogged filters reduce efficiency. Real-world tip: Keep a log of part replacements to track maintenance history.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Engine | Power generation |
| Transmission | Gear shifting |
| Brakes | Stopping mechanism |
| Suspension | Ride stability |
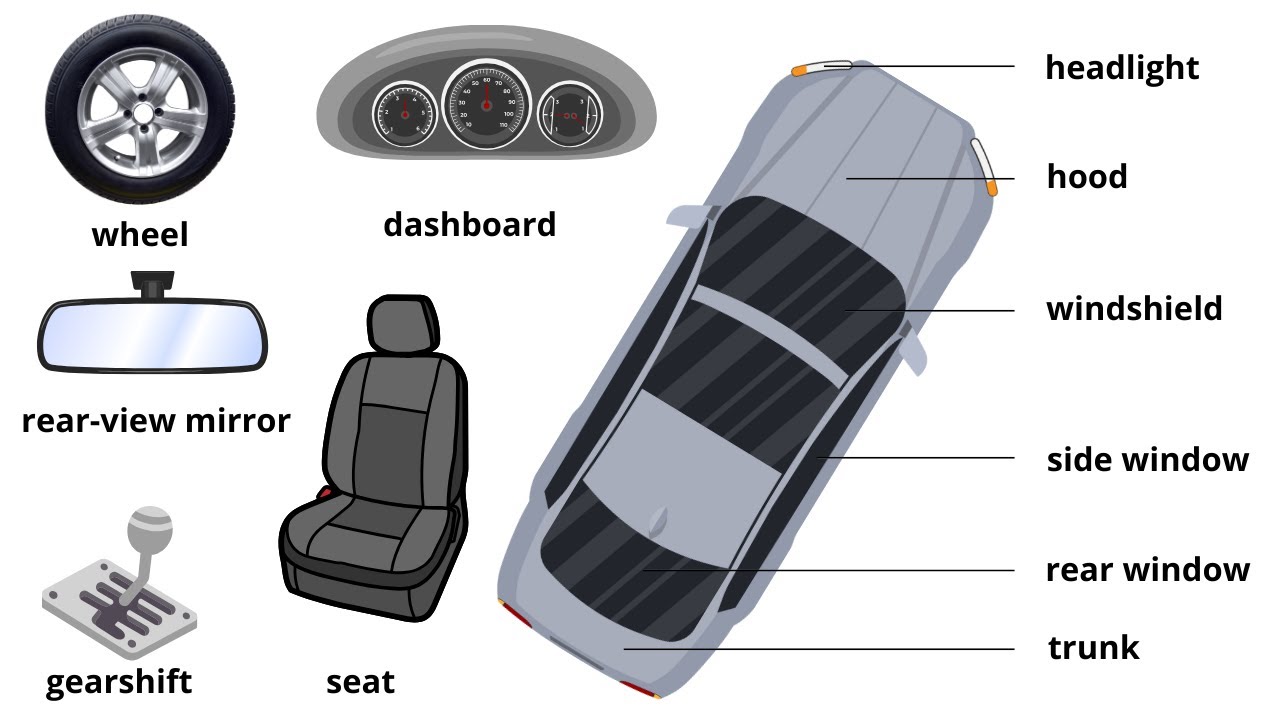
2. Learn to Identify Quality Auto Parts

Not all auto parts are created equal. Quality varies by brand, material, and manufacturing standards. Beginners should look for OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) parts, which are designed specifically for your vehicle. Aftermarket parts can be cost-effective but vary widely in quality. Check for certifications like ISO 9001 or TS 16949 to ensure reliability.
Quality Indicators
Inspect parts for durable materials, precise fitment, and warranty coverage. For example, brake pads made from ceramic tend to last longer than organic materials. Real-life example: A reputable brand’s air filter can improve fuel efficiency by up to 10% compared to cheaper alternatives.
3. Master Basic Replacement Tasks
Starting with simple replacement tasks builds confidence and skills. Beginners should tackle headlight bulbs, windshield wipers, air filters, and battery changes. These tasks require minimal tools and offer immediate results. For instance, replacing a headlight bulb takes less than 15 minutes and enhances nighttime visibility.
Step-by-Step Example: Air Filter Replacement
- Locate the air filter housing (usually near the engine).
- Remove the cover clips or screws.
- Take out the old filter and insert the new one.
- Reassemble the housing securely.
4. Understand the Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance extends a vehicle’s lifespan and prevents costly repairs. Key tasks include oil changes, fluid checks, tire rotations, and brake inspections. For example, synthetic oil changes every 7,500 miles can optimize engine performance. Neglecting maintenance leads to issues like overheating or premature wear.
Maintenance Schedule Snapshot
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 5,000-7,500 miles |
| Tire Rotation | Every 6,000 miles |
| Brake Inspection | Every 12,000 miles |
5. Utilize Diagnostic Tools for Troubleshooting

Modern vehicles are equipped with OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics) systems that monitor performance and detect issues. Beginners can use OBD-II scanners to read error codes and identify problems. For instance, a “P0420” code indicates a catalytic converter issue. These tools are affordable and user-friendly, making them essential for DIY diagnostics.
Common Diagnostic Codes
- P0300: Random misfire detected
- P0171: System too lean (Bank 1)
- P0442: Evaporative emission control system leak
6. Build a Basic Auto Repair Toolkit
Investing in essential tools is crucial for DIY repairs. A beginner’s toolkit should include wrenches, screwdrivers, socket sets, pliers, and a jack with stands. For example, a torque wrench ensures bolts are tightened to manufacturer specifications, preventing damage. High-quality tools from brands like Craftsman or Snap-On offer durability and precision.
Essential Tools Checklist
- Adjustable wrench
- Ratchet and socket set
- Pry bar
- Multimeter for electrical testing
7. Leverage Online Communities and Resources
Online forums, YouTube tutorials, and manufacturer websites are invaluable for beginners. Platforms like Reddit’s r/MechanicAdvice and YouTube channels (e.g., ChrisFix, EricTheCarGuy) offer step-by-step guides and troubleshooting tips. For example, a video on replacing brake pads can clarify complex procedures. Engaging with communities also provides support and feedback.
Recommended Resources
- Forums: CarTalk, GarageJournal
- Websites: AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts (DIY guides)
- Apps: RepairPal, Torque Pro
What are the most common auto parts to replace?
+
Common replacements include oil filters, air filters, brake pads, batteries, and windshield wipers due to regular wear and tear.
How do I know if a part is compatible with my car?
+
Check the part number, vehicle identification number (VIN), or consult your car’s manual. Online databases like AutoZone’s vehicle selector can also confirm compatibility.
Is it better to buy OEM or aftermarket parts?
+
OEM parts are recommended for guaranteed fit and quality, but high-quality aftermarket parts can be cost-effective for non-critical components.
How often should I inspect my car’s parts?
+
Inspect critical parts like brakes, tires, and fluids every 3,000 miles or as recommended in your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
Can I perform auto repairs without prior experience?
+
Yes, start with simple tasks like changing air filters or headlights. Use tutorials and seek guidance from experienced individuals for complex repairs.